Copyright © 2025 Michael Herman (Bindloss, Alberta, Canada) – Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International Public License
The Discontinuous Code Transformation Problem
Coding is a process of Discontinuous Transformation.
Orthogonal Categories
The following is the classified list of all 60 items from The Discontinuous Code Transformation Problem (with the original item numbers preserved) grouped into 5 orthogonal, spanning categories. (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Category 1 — Abstract ⇄ Formal Code (Intent and conceptual to executable code)
Category 1 — Abstract ⇄ Formal Code (Intent and conceptual to executable code)
These transformations involve moving between ideas, designs, algorithms, pseudocode, prompts and formal code.
- 1. ideas → source code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 2. ideas → pseudocode (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 3. ideas → Blocks (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 4. ideas → prompts (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 5. pseudocode → source code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 6. algorithms → source code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 7. source code → algorithms (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 21. prompts → generated code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 53. prompts → image and video code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 54. prompts → virtual people code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Category 2 — Code Representation & Structure (Different internal/code structures without altering fundamental semantics)
Category 2 — Code Representation & Structure (Different internal/code structures without altering fundamental semantics)
- 11. source code → optimized code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 12. source code → executable code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 13. source code → intermediate code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 14. source code → object code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 15. source code → virtual machine byte code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 16. source code → an AST (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 17. source code → nocode (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 25. source code → interpreted code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 26. script code → executed code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Category 3 — Code Quality & Behavioral Transformation (Improvements or regressions in code behavior, performance, structure)
Category 3 — Code Quality & Behavioral Transformation (Improvements or regressions in code behavior, performance, structure)
- 9. old source code → new source code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 10. old source code → new and changed source code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 22. source code → buggier code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 23. source code → cleaner code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 24. slow code → fast code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Category 4 — Code
Category 4 — Code 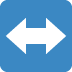 Data, Formats & External Artefacts
Data, Formats & External Artefacts
These involve mapping code to data formats, document formats, hardware descriptions, or structured data.
- 8. mathematical and arithmetic formula code → source code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 28. SQL code → datacode (CSV/XML/JSON) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 29. GraphQL/Cypher → datacode (XML/JSON) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 30. .NET objects serialized → datacode (XML/JSON) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 31. REST/HTTP codes → datacode (XML/JSON) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 32. source code → Microsoft Office document code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 37. image code → graphics code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 38. animation code → graphics code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 39. text code → audio speech code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 43. UBL code → value chain document code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 44. UBL → value chain payment instructions (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 45. UBL → value chain shipping & delivery instructions (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 55. source code → streaming code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 48. DIDs → verifiable identity code (DID Docs) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 49. Verifiable Credential code → secure, trusted document code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Category 5 — Execution Context, Platforms & Environment
Category 5 — Execution Context, Platforms & Environment
Transformations where code moves across platforms, repositories or execution environments.
- 19. local code → GitHub code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 20. GitHub code → local code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 27. shell code (cmdlets) → API codes (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 33. source code → firmware (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 34. source code → microcode (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 35. source code → silicon (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 36. source code → simulated code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 41. FTP code → file system code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 42. HTML → multi-media graphics code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 46. blockchain code → cryptocurrency codes (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 47. blockchain code → Verifiable Data Registry codes (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 50. Internet standards → interoperable protocol code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 51. source code → filesystem code (disk/storage) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 52. Office documents → filesystem code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Category 6 — Human-Cognitive & Sensory Interfaces with Code
Category 6 — Human-Cognitive & Sensory Interfaces with Code
These map between human behaviours/perceptions, neural codes, gesture codes, and symbolic codes.
- 40. SMTP code → communications neural code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 56. human gestures → sign language code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 57. sign language code → neural code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 58. source code → robot gestures (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
- 59. five senses
 neural code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
neural code (Hyperonomy Digital Lab) - 60. neural code → gestures (muscle code) (Hyperonomy Digital Lab)
 Recap of Categories with Item Count
Recap of Categories with Item Count
CategoryDescriptionRangeItems1. Abstract ⇄ Formal CodeFrom intent/design/ideas → formal code and back1–7, 21, 53–5410 items2. Code Representation & StructureFormal structure transformations11–17, 25–269 items3. Quality/BehaviorPerformance/restructuring changes9–10, 22–245 items4. Code  Data & FormatsCode as data & alternative formats8, 28–31, 32,37–39, 43–45, 48–49, 5514 items5. Execution & EnvironmentContext/platform conversions19–20, 27, 33–36, 41–42, 46–47, 50–5214 items6. Human-Cognitive InterfacesHuman signals
Data & FormatsCode as data & alternative formats8, 28–31, 32,37–39, 43–45, 48–49, 5514 items5. Execution & EnvironmentContext/platform conversions19–20, 27, 33–36, 41–42, 46–47, 50–5214 items6. Human-Cognitive InterfacesHuman signals  machine code40, 56–606 items
machine code40, 56–606 items
Not drawn to scale…